Orthographic projection
Orthographic projection (or orthogonal projection) is a means of representing a three-dimensional object in two dimensions.
It is a form of parallel projection, where all the projection lines are orthogonal to the projection plane,[1] resulting in every plane of the scene appearing in affine transformation on the viewing surface. It is further divided into multiview orthographic projections and axonometric projections. A lens providing an orthographic projection is known as an (object-space) telecentric lens.
The term orthographic is also sometimes reserved specifically for depictions of objects where the axis or plane of the object is also parallel with the projection plane,[1] as in multiview orthographic projections.
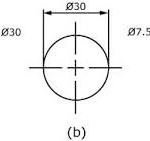
(b) is used when the circle is too small for the dimension to be easily read if it was placed inside the circle.