by admin | Jun 19, 2015 | sem3
What is RDBMS? RDBMS stands for Relational Database Management System. RDBMS is the basis for SQL, and for all modern database systems like MS SQL Server, IBM DB2, Oracle, MySQL, and Microsoft Access. A Relational database management system (RDBMS) is a database...
by admin | Jun 19, 2015 | sem3
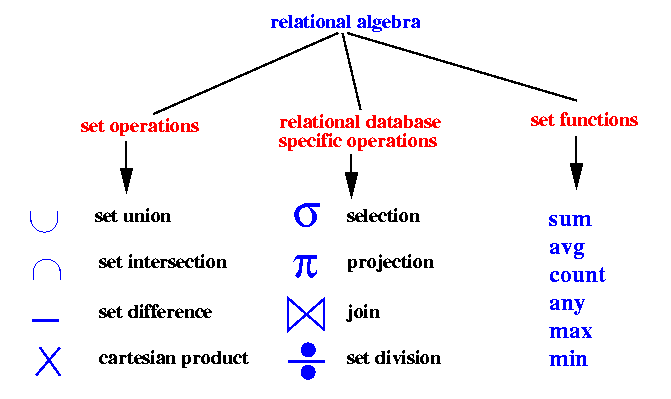
Relational Algebra Relational database systems are expected to be equipped with a query language that can assist its users to query the database instances. There are two kinds of query languages − relational algebra and relational calculus. Relational Algebra...
by admin | Jun 19, 2015 | sem3
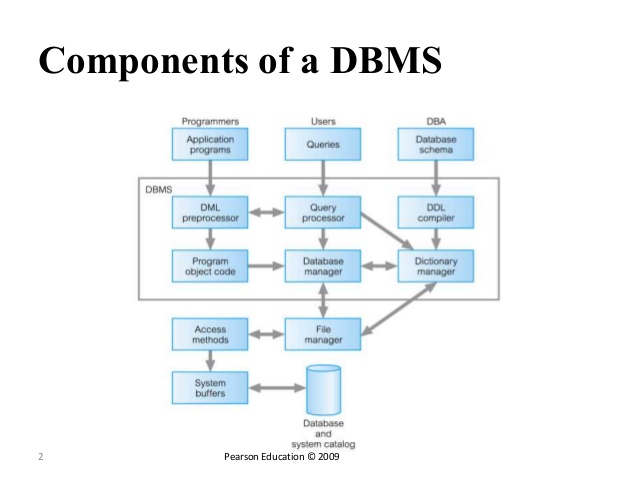
Components of dbms A typical structure of components of DBMS and relationships between them is show. The DBMS software is partitioned into several modules. Each module or component is assigned a specific operation to perform. Some of the functions of the DBMS are...
by admin | Jun 17, 2015 | sem4
Purpose of Database Systems To see why database management systems are necessary, let’s look at a typical “file-processing system” supported by a conventional operating system.The application is a savings bank: Savings account and customer records...
by admin | Jun 17, 2015 | sem3
Functional Dependency Functional dependency (FD) is a combinations of constraints between 2 attributes in a relation. Functional dependency explians that if two records have same values for attributes A1, A2,…, An, then those two records must have to have same...
by admin | Jun 17, 2015 | sem3
Domain key normal form After a SQL database is in third normal form, you’ve eliminated most, but not all, chances of modification anomalies. Normal forms beyond the third are defined to squash those few remaining bugs. Domain key normal form (DK/NF) Boyce-Codd normal...


